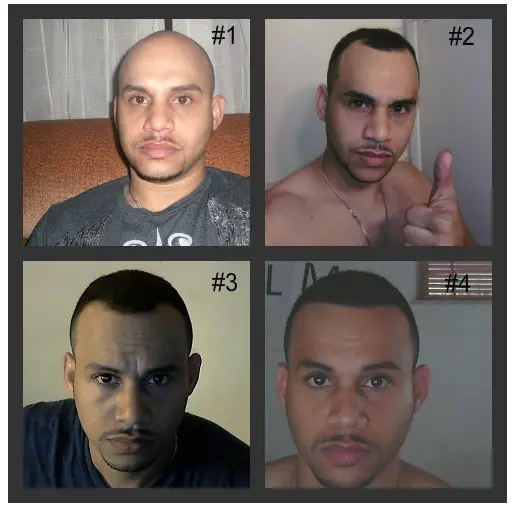
There are many ways in which hair loss can occur, but one type is retrograde alopecia in female and male, which can be easily noticed or diagnosed until you’ve experienced it. What causes retrograde alopecia? Why does this type of DPA hair loss often go unnoticed? And what are the best treatment options for stopping this kind of crown of your-head hair loss? This article will answer these questions on retrograde alopecia, its causes, signs, and treatment options.
What is Retrograde Alopecia?
There are many different types of alopecia, but the most common is Androgenetic Alopecia.
Retrograde Alopecia is a type of Androgenetic Alopecia, which means that it’s caused by the hormone DHT. The difference between Retrograde Alopecia and other types of Androgenetic Alopecia is that it affects the hairline at the back of the head rather than on top.
Symptoms and Signs of Retrograde Alopecia
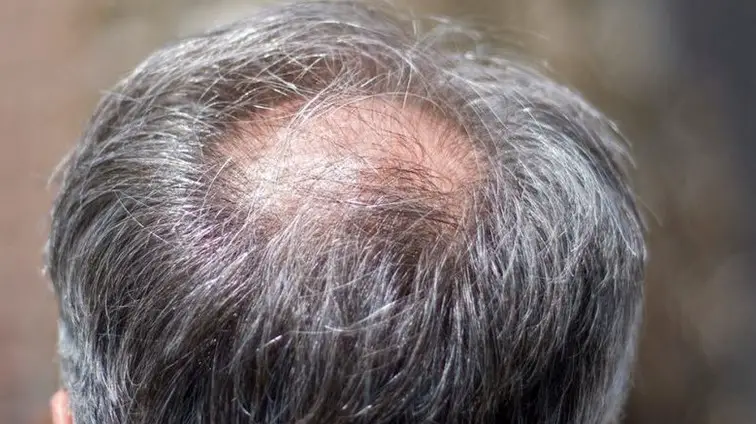
Retrograde Alopecia is a condition where the hair starts to fall out from the scalp in a circular pattern. It can be caused by many different factors, but the most common cause is stress.
The first symptom of Retrograde Alopecia is usually hair loss that starts at the back and top of the head. The hair will then start to thin and eventually stop growing altogether. You may also start to notice small bald patches at the back of your head or on your forehead.
If you’re experiencing these symptoms, it’s important to see a doctor as soon as possible to rule out other conditions like an autoimmune disorder or thyroid disease.
Signs are:
- Small bald hair patches on the crown or scalp.
- Patches area may get bigger and grow jointly into a bald spot on the crown
- Hair might grows back in one spot and fall out in another
- You lose more hair over a short period
- When cold weather, more hair is lost
- Fingernails and your toenails become red, flaky, and pitted
- Hair falls out little by little
- Receding hairline
Retrograde Alopecia Treatments and Solutions
Retrograde Alopecia is a medical condition in which hair follicles are destroyed, resulting in hair loss. There are many treatments and solutions to combat this condition.
The most common treatment for Retrograde Alopecia is minoxidil (rogaine) and finasteride (propecia). It can be used both as a topical solution or as an oral medication. Minoxidil does not cure the condition, but it does stimulate hair growth and can slow down the progression of the disease. Other treatments include various medications, scalp injections, laser red light therapy for hair loss, and Retrograde Alopecia hair transplants.
In some cases, the best treatment might not be a medical one at all – it might be something as simple as changing your diet or using supplements that promote healthy hair growth.
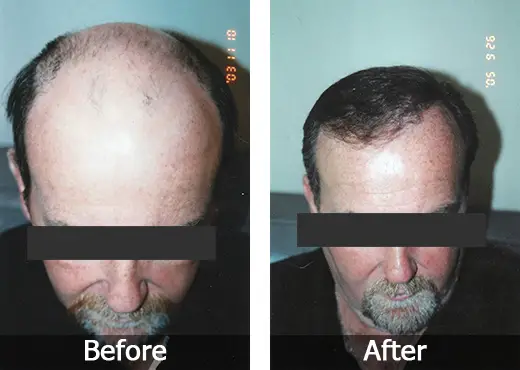
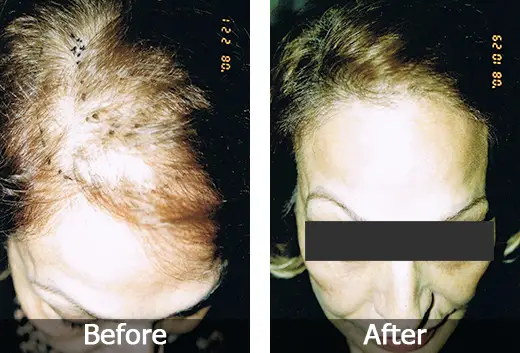
Retrograde alopecia before and after
Retrograde alopecia is a rare type of hair loss that occurs when the hair follicles are attacked by the immune system. It is also known as alopecia areata retrogressiva, and can happen at any age.
Retrograde alopecia can be triggered by a number of factors, such as stress, illness, or even hormonal changes. It typically starts with a small patch of baldness in the scalp and then spreads over time to other areas of the head. A person with this condition may experience some itching or tingling sensations on their scalp before noticing any hair loss.
What is the causes of retrograde alopecia?
Retrograde alopecia is a rare form of hair loss. It is caused by the inflammation of the hair follicles. The inflammation can be caused by an autoimmune disorder, a skin condition, or a medication.
Other causes are:
- Family history/genetics
- Hormones/DHT
- Traction alopecia (al-oh-pee-sha)
In other words, Retrograde hair loss is an uncommon type of baldness at the crown in which the follicles that produce new hairs begin to shrink. This shrinking process causes the hairs to eventually stop growing altogether. The condition is also called alopecia areata retrogressive. Retrograde alopecia causes can include autoimmune issues, trauma, and stress.
is retrograde alopecia permanent?
The answer to this question is not a cut-and-dry yes or no. It depends on what caused the hair loss in the first place. Retrograde alopecia can be permanent if you were born with it or if it results from your thyroid hair loss, the hair will not grow back, and the condition is usually permanent. However, some of the best hair loss products for treating advanced crown balding stages may help slow down the progression of this condition. Otherwise, losing hair due to retrograde alopecia may only be temporary.
What are the 4 types of alopecia?
Alopecia is a condition in which the hair on the scalp and body starts to fall out.
Types of alopecia are:
- Alopecia areata
- Alopecia totalis
- Alopecia universalis
- Androgenetic alopecia
Another type is DUPA hair loss that is not mention alot.
Does retrograde alopecia get worse?
The condition is not life-threatening, but it can cause significant distress to those who have it. It is characterized by hair loss that starts at the head and progresses towards the feet, with different degrees of severity among cases.
The good news is that retrograde alopecia does not get worse with early hair loss treatment. The bad news is that the condition can worsen if left untreated. If you notice hair loss in patches or have bald patches, consider getting a thyroid test. Thyroid issues are often to blame for retrograde alopecia. To prevent hair loss from worsening, ensure your thyroid levels are where they should be by seeing an endocrinologist and adjusting medication as necessary.
Retrograde alopecia vs Dupa
The difference between retrograde alopecia vs Dupa is that dupa affects hair follicles that have not been transplanted yet. Dupa results in changes to the structures of the hair follicle cells. The exact cause of dupa is still unknown. In some cases, patients suffering from an underactive thyroid can develop both dupa and retrograde alopecia. However, these two conditions are not necessarily linked together. In addition to a well-functioning thyroid gland, there must be other factors, such as a traumatic event, for someone to develop retrograde alopecia.
Conclusion: Retrograde Alopecia – What You Need to Know
What is Retrograde Alopecia?
Retrograde alopecia is a condition in which hair loss occurs on the back of the head. It is caused by traction on the hair roots.
How do you get it?
It can be caused by pulling, braiding, or even wearing tight hairstyles that put tension on the hair follicles.
What are the symptoms?
The symptoms are usually not noticeable until significant hair loss has already occurred. The first sign may be a small bald spot or thinning of the hairline at the back of your head. Some people may experience pain in their scalp as well as itching, redness, and inflammation.
How do you treat it?
The treatment for retrograde alopecia begins with consulting with a dermatologist to determine if there is underlying medical condition causing it and to prescribe treatments for these conditions. In some cases, surgery may be required to remove any scar tissue.
- AI Powered Bald Filter Online 2024: See Yourself with No Hair! - January 19, 2024
- Harklinikken Bad Reviews 2024: Analyzing Negative Feedbacks - January 18, 2024
- How to Get the Alex Eubank Hair | Step-By-Step Tutorial 2024 - January 18, 2024